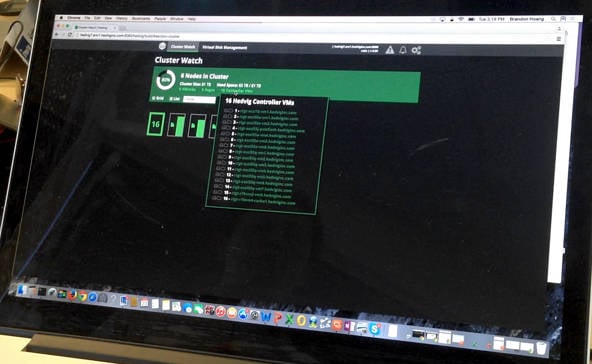
ClusterWatch Mac OS
The following tables compare general and technical information for notable computer clustersoftware. This software can be grossly separated in four categories: Job scheduler, nodes management, nodes installation and integrated stack (all the above).
General information[edit]
Clusterwatch Mac Os Catalina
Configure alert thresholds for Cassandra cluster-wide, table, and operating system metrics in the Alerts area of OpsCenter. This proactive monitoring feature is available for DataStax Enterprise clusters. Advanced system alert metrics. Configure advanced system metrics for memory, CPU, and disk metrics on Linux or Mac OS X.
Clustertruck MacOSX is a new type of platformer. It leads you onto a speeding highway where you use agility, speed and acrobatics making your way through crazy levels in a game of “the floor is lava” matched up with unpredictable, speeding trucks! Clustertruck MacOSX features a campaign mode whose evilness gradually increases. The difficulty of game sky-rockets when dangers such as swinging lasers, hammers and flamethrowers are added! The idmapper on the Mac has to map the user@dnsdomain UTF-8 strings sent from the server to known entities within OS X's own Directory Services framework. Other OSes like Linux use a separate daemon (idmapd) to map those strings to UIDs and GIDs. OS X has to do the same, but the idmapper does not seem to work correctly, yet, on OS X 10.8, or 10.9. Xsan is a cluster file system for Mac OS X. Its primary use is to allow multiple fiber channel hosts to access multiple Xserve RAIDs with the use of a fibre channel switch. 1 Release history 2 References 3 External links Apple Inc. First announced Xsan in 2004. Xsan 1.0 began shipping on January 4, 2005. Xsan 1.2 shipped in May 2006. Xsan 1.4 shipped on August 7, 2006. Xsan 2 shipped on.
| Software | Maintainer | Category | Development status | ArchitectureOCS | High-Performance/ High-Throughput Computing | License | Platforms supported | Cost | Paid support available |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accelerator | Altair | Job Scheduler | actively developed | Master/worker distributed | HPC/HTC | Proprietary | Linux, Windows | Cost | Yes |
| Amoeba | No active development | MIT | |||||||
| Base One Foundation Component Library | Proprietary | ||||||||
| DIET | INRIA, SysFera, Open Source | All in one | GridRPC, SPMD, Hierarchical and distributed architecture, CORBA | HTC/HPC | CeCILL | Unix-like, Mac OS X, AIX | Free | ||
| Enduro/X | Mavimax, Ltd. | Job/Data Scheduler | actively developed | SOA Grid | HTC/HPC/HA | GPLv2 or Commercial | Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, Solaris, AIX | Free / Cost | Yes |
| Ganglia | Monitoring | actively developed | BSD | Unix, Linux, Windows NT/XP/2000/2003/2008, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, DragonflyBSD, Mac OS X, Solaris, AIX, IRIX, Tru64, HPUX. | Free | ||||
| Globus Toolkit | Globus Alliance, Argonne National Laboratory | Job/Data Scheduler | actively developed | SOA Grid | Linux | Free | |||
| Grid MP | Univa (formerly United Devices) | Job Scheduler | no active development | Distributed master/worker | HTC/HPC | Proprietary | Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, Solaris | Cost | |
| Apache Mesos | Apache | actively developed | Apache license v2.0 | Linux | Free | Yes | |||
| Moab Cluster Suite | Adaptive Computing | Job Scheduler | actively developed | HPC | Proprietary | Linux, Mac OS X, Windows, AIX, OSF/Tru-64, Solaris, HP-UX, IRIX, FreeBSD & other UNIX platforms | Cost | Yes | |
| NetworkComputer | Runtime Design Automation | actively developed | HTC/HPC | Proprietary | Unix-like, Windows | Cost | |||
| OpenHPC | OpenHPC project | all in one | actively developed | HPC | Linux (CentOS) | Free | No | ||
| OpenLava | Teraproc | Job Scheduler | actively developed | Master/Worker, multiple admin/submit nodes | HTC/HPC | GPL | Linux | Free | Yes |
| PBS Pro | Altair | Job Scheduler | actively developed | Master/worker distributed with fail-over | HPC/HTC | AGPL or Proprietary | Linux, Windows | Free or Cost | Yes |
| Proxmox Virtual Environment | Proxmox Server Solutions | Complete | actively developed | Open-source AGPLv3 | Linux, Windows, other operating systems are known to work and are community supported | Free | Yes | ||
| Rocks Cluster Distribution | Open Source/NSF grant | All in one | actively developed | HTC/HPC | OpenSource | CentOS | Free | ||
| Popular Power | |||||||||
| ProActive | INRIA, ActiveEon, Open Source | All in one | actively developed | Master/Worker, SPMD, Distributed Component Model, Skeletons | HTC/HPC | GPL | Unix-like, Windows, Mac OS X | Free | |
| RPyC | Tomer Filiba | actively developed | MIT License | *nix/Windows | Free | ||||
| SLURM | SchedMD | Job Scheduler | actively developed | HPC/HTC | GPL | Linux/*nix | Free | Yes | |
| Spectrum LSF | IBM | Job Scheduler | actively developed | Master node with failover/exec clients, multiple admin/submit nodes, Suite addOns | HPC/HTC | Proprietary | Unix, Linux, Windows | Cost and Academic - model - Academic, Express, Standard, Advanced and Suites | Yes |
| Oracle Grid Engine (Sun Grid Engine, SGE) | Univa | Job Scheduler | active Development moved to Univa Grid Engine | Master node/exec clients, multiple admin/submit nodes | HPC/HTC | Proprietary | *nix/Windows | Cost | |
| SynfiniWay | Fujitsu | actively developed | HPC/HTC | ? | Unix, Linux, Windows | Cost | |||
| TORQUE Resource Manager | Adaptive Computing | Job Scheduler | actively developed | Proprietary | Linux, *nix | Cost | Yes | ||
| UniCluster | Univa | All in One | Functionality and development moved to UniCloud (see above) | Free | Yes | ||||
| UNICORE | |||||||||
| Univa Grid Engine | Univa | Job Scheduler | actively developed | Master node/exec clients, multiple admin/submit nodes | HPC/HTC | Proprietary | *nix/Windows | Cost | |
| Xgrid | Apple Computer | ||||||||
| Software | Maintainer | Category | Development status | Architecture | High-Performance/ High-Throughput Computing | License | Platforms supported | Cost | Paid support available |
Table explanation
- Software: The name of the application that is described
Technical information[edit]
| Software | Implementation Language | Authentication | Encryption | Integrity | Global File System | Global File System + Kerberos | Heterogeneous/ Homogeneous exec node | Jobs priority | Group priority | Queue type | SMP aware | Max exec node | Max job submitted | CPU scavenging | Parallel job | Job checkpointing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enduro/X | C/C++ | OS Authentication | GPG, AES-128, SHA1 | None | Any cluster Posix FS (gfs, gpfs, ocfs, etc.) | Any cluster Posix FS (gfs, gpfs, ocfs, etc.) | Heterogeneous | OS Nice level | OS Nice level | SOA Queues, FIFO | Yes | OS Limits | OS Limits | Yes | Yes | No |
| HTCondor | C++ | GSI, SSL, Kerberos, Password, File System, Remote File System, Windows, Claim To Be, Anonymous | None, Triple DES, BLOWFISH | None, MD5 | None, NFS, AFS | Not official, hack with ACL and NFS4 | Heterogeneous | Yes | Yes | Fair-share with some programmability | basic (hard separation into different node) | tested ~10000? | tested ~100000? | Yes | MPI, OpenMP, PVM | Yes |
| PBS Pro | C/Python | OS Authentication, Munge | Any, e.g., NFS, Lustre, GPFS, AFS | Limited availability | Heterogeneous | Yes | Yes | Fully configurable | Yes | tested ~50,000 | Millions | Yes | MPI, OpenMP | Yes | ||
| OpenLava | C/C++ | OS authentication | None | NFS | Heterogeneous Linux | Yes | Yes | Configurable | Yes | Yes, supports preemption based on priority | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Slurm | C | Munge, None, Kerberos | Heterogeneous | Yes | Yes | Multifactor Fair-share | yes | tested 120k | tested 100k | No | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Spectrum LSF | C/C++ | Multiple - OS Authentication/Kerberos | Optional | Optional | Any - GPFS/Spectrum Scale, NFS, SMB | Any - GPFS/Spectrum Scale, NFS, SMB | Heterogeneous - HW and OS agnostic (AIX, Linux or Windows) | Policy based - no queue to computenode binding | Policy based - no queue to computegroup binding | Batch, interactive, checkpointing, parallel and combinations | yes and GPU aware (GPU License free) | > 9.000 compute hots | > 4 mio jobs a day | Yes, supports preemption based on priority, supports checkpointing/resume | Yes, fx parallel submissions for job collaboration over fx MPI | Yes, with support for user, kernel or library level checkpointing environments |
| Torque | C | SSH, munge | None, any | Heterogeneous | Yes | Yes | Programmable | Yes | tested | tested | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| Univa Grid Engine | C | OS Authentication/Kerberos/Oauth2 | Certificate Based | Integrity | Arbitrary, e.g. NFS, Lustre, HDFS, AFS | AFS | Fully heterogeneous | Yes; automatically policy controlled (e.g. fair-share, deadline, resource dependent) or manual | Yes; can be dependent on user groups as well as projects and is governed by policies | Batch, interactive, checkpointing, parallel and combinations | Yes, with core binding, GPU and Intel Xeon Phi support | commercial deployments with many tens of thousands hosts | >300K tested in commercial deployments | Yes; can suspend job on interactive usage | Yes, with support of arbitrary parallel environments such as OpenMPI, MPICH 1/2, MVAPICH 1/2, LAM, etc. | Yes, with support for user, kernel or library level checkpointing environments |
| Software | Implementation Language | Authentication | Encryption | Integrity | Global File System | Global File System + Kerberos | Heterogeneous/ Homogeneous exec node | Jobs priority | Group priority | Queue type | SMP aware | Max exec node | Max job submitted | CPU scavenging | Parallel job | Job checkpointing |
Table Explanation
- Software: The name of the application that is described
- SMP aware:
- basic: hard split into multiple virtual host
- basic+: hard split into multiple virtual host with some minimal/incomplete communication between virtual host on the same computer
- dynamic: split the resource of the computer (CPU/Ram) on demand
History and adoption[edit]
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
External links[edit]
It was two decades ago to the day—March 24, 2001—that Mac OS X first became available to users the world over. We're not always big on empty sentimentality here at Ars, but the milestone seemed worthy of a quick note.
Of course, Mac OS X (or macOS 10 as it was later known) didn't quiteClusterwatch Mac Os X
survive to its 20th birthday; last year's macOS Big Sur update brought the version number up to 11, ending the reign of X.But despite its double life on x86 and ARM processors and its increasingly close ties to iOS and iPadOS, today's macOS is still very much a direct descendant of that original Mac OS X release. Mac OS X, in turn, evolved in part from Steve Jobs' NeXT operating system—which had recently been acquired by Apple—and its launch was the harbinger of the second Jobs era at Apple.
Cheetah, Mac OS X's initial release, was pretty buggy. But it introduced a number of things that are still present in the operating system today. Those included the dock, which—despite some refinements and added features—is still fundamentally the same now as it ever was, as well as the modern version of Finder. And while macOS has seen a number of UI and design tweaks that have changed over time, the footprints of Cheetah's much-hyped Aqua interface can still be found all over Big Sur.
AdvertisementOS X brought many new features and technologies we now take for granted, too. For example, it enabled Apple's laptops to wake up from sleep immediately, and it introduced dynamic memory management, among other things.
Clusterwatch Mac Os Download
Mac OS X's greatest impact in retrospect may be in the role it had in inspiring and propping up iOS, which has far surpassed macOS as Apple's most widely used operating system. And indeed, macOS lives in a very different context today than it did in 2001. It was recently bumped from the No.2 operating system spot globally by Google's Chrome OS, ending a very long run for Mac OS as the world's second-most popular desktop operating system in terms of units shipped.
The most popular desktop operating system in 2021 is Windows, just as it was in 2001, but the most popular OS overall is Google's Android, which has dramatically larger market share in the mobile space than iOS does.So while Mac OS X's influence is profound, it exists today primarily as a support for iOS, which is also itself not the most popular OS in its category. Despite Apple's resounding success in the second Steve Jobs era, as well as in the recent Tim Cook era, the Mac is still a relatively niche platform—beloved by some, but skipped by much of the mainstream.
Clusterwatch Mac Os 11
After 20 years, a lot has changed, but a whole lot has stayed the same.